Basic Research
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
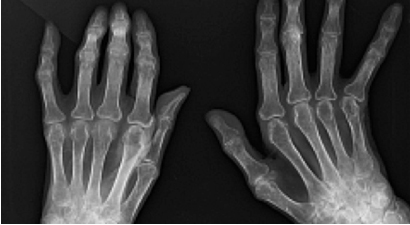
Rheumatoid arthritis(RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized synovial hyperplasia and chronic inflammation, which lead to the progressive destruction of cartilage and bone in the joint. Numerous studies have reported that administration of various type of MSCs improve arthritis symptoms in animal models, by paracrine mechanism.
However, the therapeutic effects of the secreted factors alone, without the cell graft, have been uncertain.
Here we show that a single intravenous administration of serum-free conditioned medium(CM) from human deciduous dental pulp stem cell(SHEDCM) into and anti-collagen type II antibody – induced arthritis(CAIA), a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis(RA), markedly improved the arthritis symptoms and joint destruction.⑨

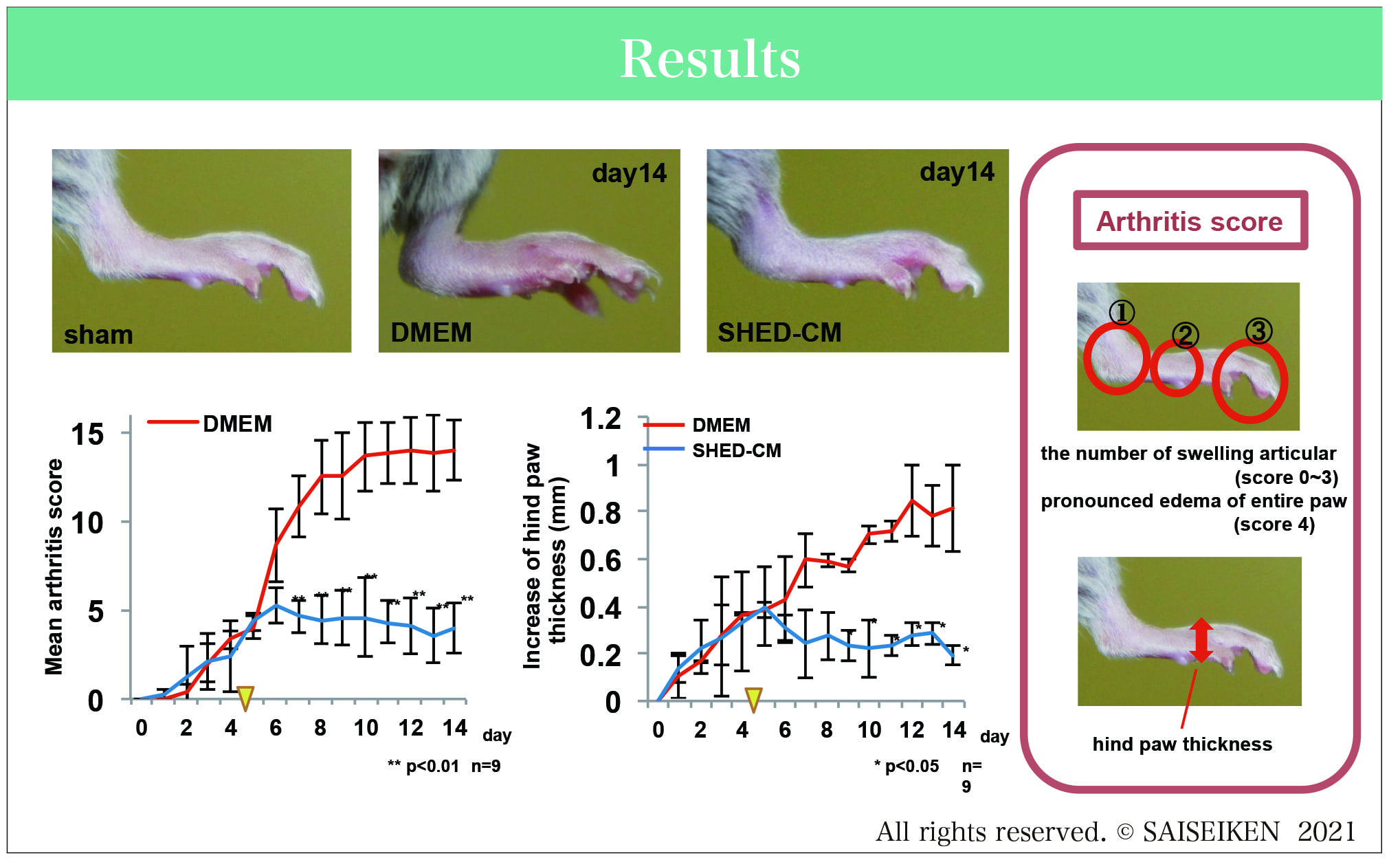
In macro-finding after confirming early arthritis symptoms on day 5, the CAIA mice were treated with a single intravenous injection of SHEDCM or DMEM. By day 8 DMEM- and BMSC-treated mice respectively displayed severe and moderate swelling encompassing the ankle, foot and digits. Notably, the SHEDCM treated mice exhibited minimal paw swelling.
No adverse effects were observed during the experimental period.
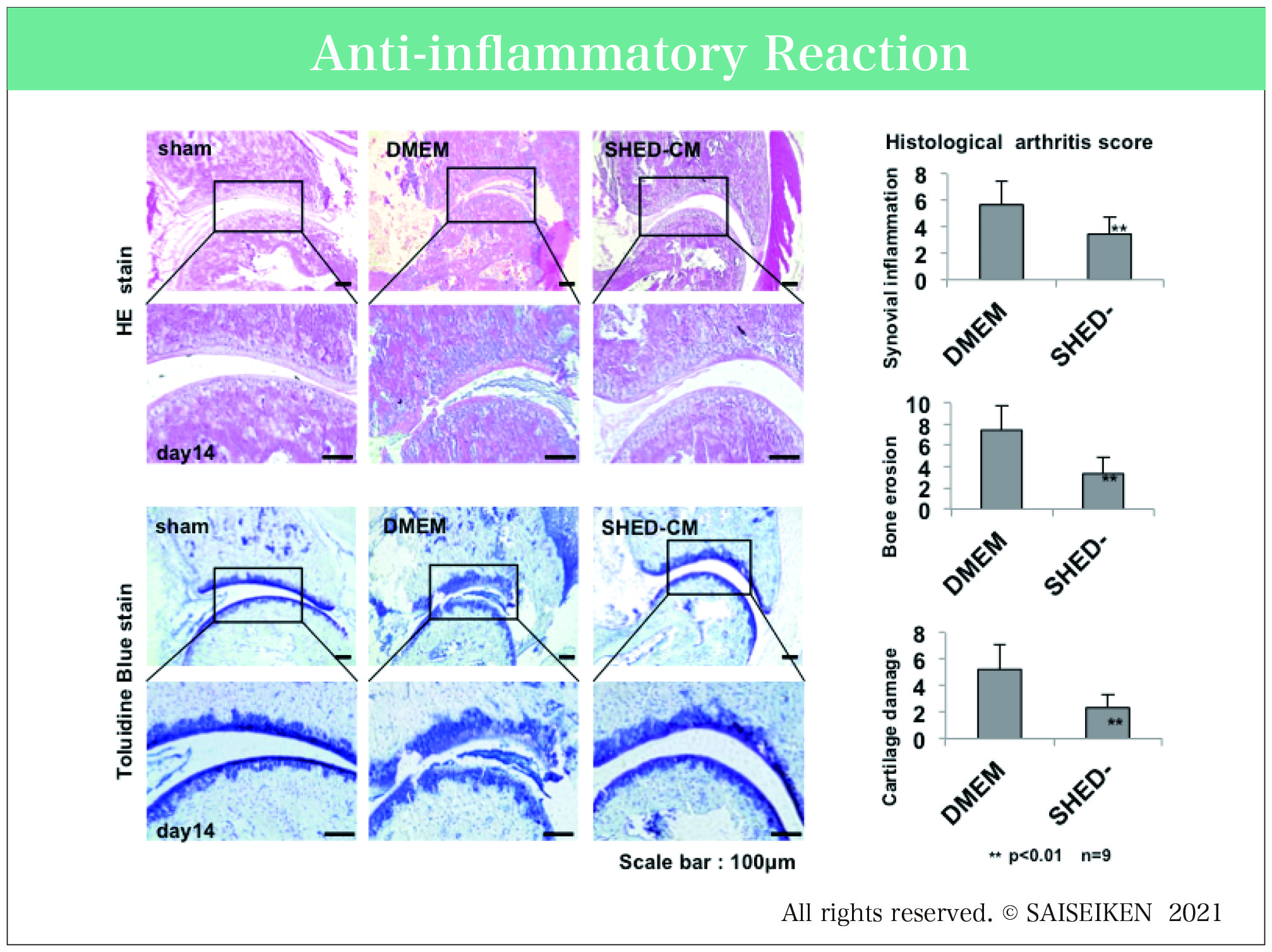
Histological analysis (performed on day 14)of the ankle joints of DMED-treated mice showed profound tissue damage, including hyperplasia, inflammatory cell infiltration, pannus formation, and intense bone and cartilage destruction.
Middle tissue destruction was observed in the BMSCCM-treated mice. In contrast, SHEDCM-treated mice exhibited markedly reduced synovial inflammation and bone and cartilage destruction. The quantitative histological scores of synovial inflammation, bone erosion, and cartilage damage were all significantly lower in SHEDCM treated mice that in BMSCCM- or DMEM-treated mice.
Thus, SHEDCM may represent a novel anti-inflammatory and reparative therapy for RA.
(Ishkawa,J. rt al: Factors secreted from pulp stem cell show mutifaceted benefit for treating experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Bone. 2015)
Based on the therapeutic promise in pre-clinical studies , SHEDCM have entered early phase clinical testing in patients with RA.
We investigated the single arm efficacy test of the conditioned medium therapy using SHEDCM for the people with RA.
We involved 19 patients ( 20 knees, 45-65 years with K-L grade 1-3 knee OA ) with symptoms of knee joint pain and/or functional limitations despite non-surgical treatment for a minimum of 3 months.
They continued to take their regular RA medication during the course of the study. The patients received SHEDCM treatment via intravenous injection, Compared with the conditions before treatment the patients who received the SHEDCM treatment showed a significant remission of the condition. After CM treatment , no serious adverse events were observed during the trial.
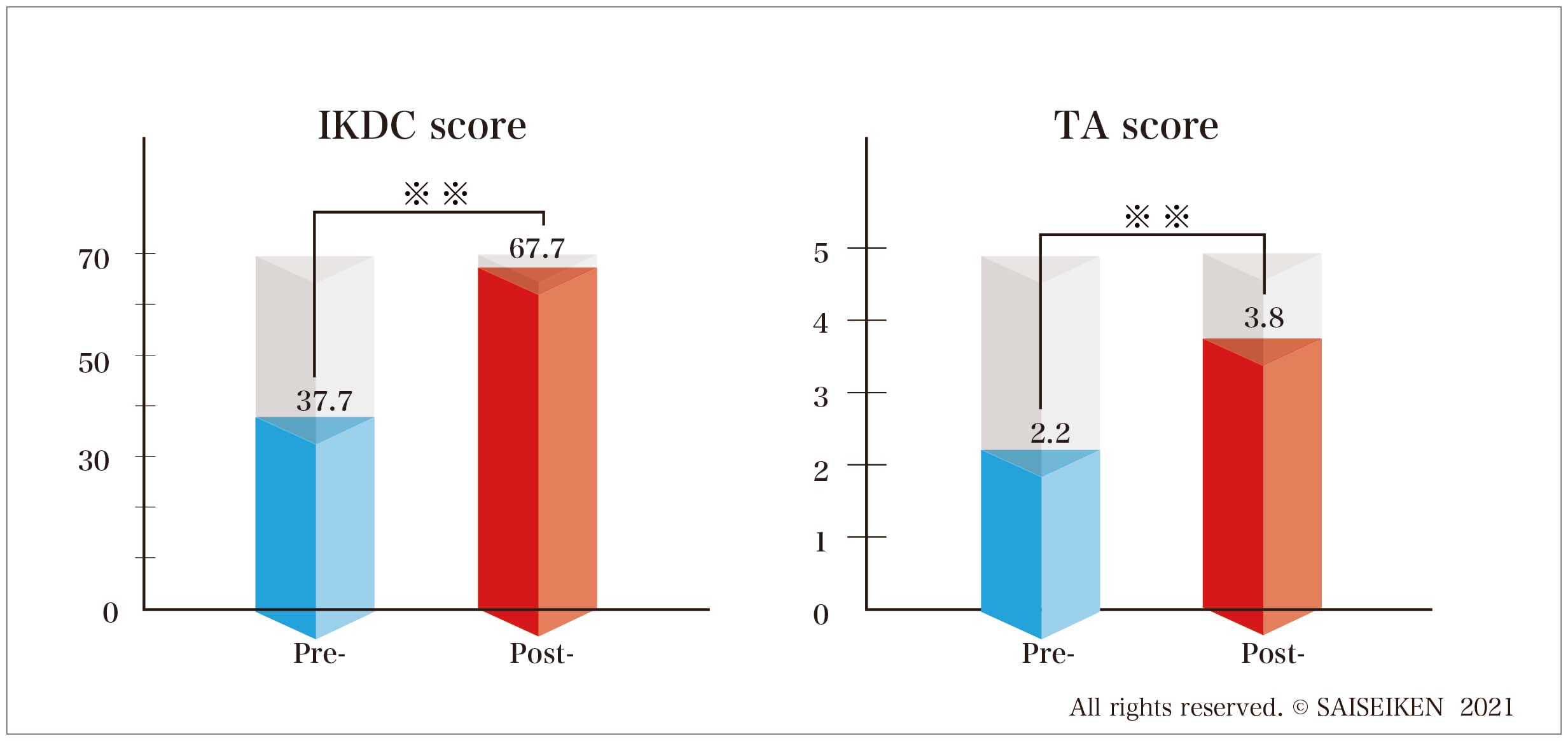
The team measured the extent remission using International Knee Documentation (IKDC)score and Tegner Activity Scale.
Both scores showed significant improvements in patients from 37.7 to 67.3 by IKDC score and from 2.2 to 3.8 by TA scale , with 74.5% of them expressing better satisfaction. In addition , age and lesion size were identified as independent factors affecting clinical out comes. Patients over 60 years age with lesion size >6.0 ㎠ showed less favorable results.
Although there were some variations in the results due to those factors, the overall clinical outcomes of CM therapy in OA patients were encouraging, with successful results.
The conditioned Medium therapy is still a relatively new area of research . However , early trials suggest that such therapies may be effective against a range of autoimmune conditions, including RA. The conditioned medium therapy seems to show promise for the treatment of RA. Studies show that CM can suppress immune system overactivity, which helps chronic inflammation.